SAP S/4HANA Intelligent Enterprise Architectures implement end-to-end business processes with intelligent technologies and innovations on hybrid multi-cloud Business Technology Platforms like SAP BTP, Microsoft Azure or Amazon AWS. These well designed SAP S/4HANA Cloud enterprise architectures describe hybrid multi-cloud components with relationships within complex heterogeneous systems.
Furthermore, SAP Enterprise Architecture helps to manage transformations with the SAP S/4HANA Cloud Activate Innovation Service methology from business vision to business process implementation with aligned IT systems on hybrid multi-cloud environments.
Hybrid multi-cloud Business Technology Platforms like SAP BTP, Azure or AWS are the foundation of intelligent SAP S/4HANA Cloud Enterprise Architectures with outstanding innovations.
Cloud services on SAP BTP, Azure or AWS enable the alignment of data-driven business processes and technical IT systems with intelligent technologies and capabilities like automation or decision taking based on recommendations and insights. Cloud platforms offer data as important valuable asset for companies, in a variety of business processes or as complementary product.
Agile SAP Enterprise Architecture development combines Design Thinking, SAP Activate with modern design tools like LeanIX based on a tailored TOGAF framework.
SAP Intelligent Enterprise Architecture development looks holistically on subsystems within the enterprise to realize non-local, enterprise-wide changes like S/4HANA transformations. Deliverables describe fundamental component structures, their relationships, also with external systems, and guide with principles the design and evolution over time.
Common vocabularies help to align the communication between business and IT about technical implementations of end-to-end business processes with documented decisions or discussions. Well designed, integrated cloud enterprise architectures reduce the complexity of IT environments and operationalize innovations with SAP intelligent technologies.
SAP Enterprise Architecture Methodology Reference Content is available with the SAP Signavio Process Explorer and provides standardized content divided into Reference Business (RBA) and IT Solution (RSA) architecture domains.
The reference content is divided into Capability, Process, Data and Organization views on different models. Relationships between Business and Solution models, visualized in the diagram below, allow to translate between business and solution architecture artifacts.

SAP Cloud Intelligent Enterprise Architecture scope is structured into Business, Data, Application and Technology domains which are aligned with the TOGAF® Enterprise Architecture Development Method (ADM) cycle.

As central process, requirement management describes what business should be able to do and which functionality needs to be implemented with capabilities of architectural building blocks. Business processes are realizations of these capabilities, controlled by business operating models which define business roles with responsibilities.
Application and technology layers manage technical aspects of business process implementation like standard or custom development approachesl, software usage models or cloud strategies.
Integrated Enterprise Architecture and Business Process Model (BPM) toolchains enable companies to implement their people centric business strategy. Business Process Management is focused mainly on the design of business processes to enable business capabilities. Enterprise Architecture tools like LeanIX are focused more on technical aspects like realizing technical solutions with intelligent applications based on data-driven processes and innovative technologies.
Capabilities like advanced visualization with different views, data integration and version control are some important selection criteria for enterprise architecture tools.

Integrated Enterprise Architecture and BPM tools enable options to measure the impact of architectural design on business solutions and vice versa.
Strategic and operational excellence are two concepts to improve business success. Operational excellence is a bottom-line growth approach to manage business and operational processes systematically with efficient spending and managing operating costs to improve the net income. On the other side, strategic excellence is focused on top-line growth with increasing revenue of existing or new sales channels.
Business and technology can both be drivers of business excellence within different innovation areas. Business driven innovations typically explore new business models with disruptive innovations to improve strategic excellence and new business capabilities.
Business driven SAP projects focus more on work products of the Business Architecture Phase and Strategy Maps, in contrast to technology driven SAP Enterprise Architecture projects with focus on technical Solution Architectures of ADM phases C/D.
Operational excellence can be implemented with incremental innovations, to improve proven business models and IT management, with optimization or standardization based on suitable solutions like S/4HANA public cloud.
The SAP Enterprise Architecture framework is based on the TOGAF®
Methodology and offers Reference Architecture Content as standardized
business architecture definition (RBA) and guidance for solution
architectures (RSA) with capability, process and data model content
types.
SAP Reference Business and Solution Architecture content is available as
part of the One Process Acceleration Layer practice in the Signavio
Process Explorer.
Business capabilities define what the business does to generate value and enable business activities of business processes which create values or outcomes. Solution Capabilities are implementations of Business Capabilities assigned to one or more solution components in Solution Process Models.
Deliverables of the development process are provided as work products in the form of matrices, lists or diagrams. Some main deliverables define the current (base) and future state (target) architecture, together with a gap analysis with action items and a roadmap to reach the target state with times, sequences and milestones.
The MetroMap below visualizes work products for Lean SAP Enterprise Architecture projects with arrows as input / output dependencies highlight a fast lane to a minimal viable enterprise architecture. Iterations, between phases and for work products like Risk Analysis, are considered as part of the ADM process which is not a sequential approach.

One unique consistent target architecture can be displayed in different views with specific detail levels for different purposes and stakeholders. These views can be implemented with different kind of diagrams for static or dynamic content.
ADM is the core component of the TOGAF® Enterprise Architecture framework. The phases of the ADM process template require input and deliver work products as deliverables as result of the architecture development process.
Phase to decide how to tailor the SAP Enterprise Architecture Framework with the SAP Enterprise Architecture content.

The ADM preliminary phase expects business and architectural inputs to determine and establish architecture capabilities. Defined business strategies or business principles guide companies through business decisions and actions.
The Request for Architecture Work is a high level document as possible output of the Preliminary phase to trigger of the start of the ADM cycle.
Enterprise Architecture projects get established and initiated in the ADM Architecture Vision phase. Main deliverable of this phase is the Statement of Architectural Work with a high-level vision of the delivered capabilities and business values of the investment (project).

SAP Enterprise Architecture Stakeholder Matrix
Organize stakeholder management and create communication plan to keep stakeholders involved, informed and able to raise concerns about the SAP Intelligent Enterprise architectural work. The Stakeholder Matrix reflects the identification, analysis and categorization as contributors, approvers or consumers of work products.

SAP Enterprise Architecture Business Strategy Map
SAP Enterprise Architecture Business Strategy Maps provide a business context for architectural work and describe how companies meet their strategic priorities through goals, value drivers and initiatives.

SAP Enterprise Framework - Business Model Canvas
Business models describe how companies create, deliver and capture value. The Business Model Canvas (BMC)1 diagram is a SAP Enterprise Framework work product which visualizes key areas of current and intended business models.

Typically the business model design starts with the definition of the value proposition, followed by specifying customer key areas of the BMC frontstage.
Statement of Architectural work
Statement of Architectural Work defines the relevant architectural scope, based on the business context of the Strategy Map, as input for Architecture principles, Risk Analysis, Solution Context, use Case Blueprint Diagram.
Typically successful SAP Intelligent Enterprise Architecture project implementation is measured against the Statement of Architecture Work.
Row 1-3 describe the scope of the architectural work with business objectives, activities, roles and responsibilities, based on the business input of strategy map. Row 4-6 have project management characteristics.

Enterprise Architecture Principles
The Enterprise Architecture Principles catalog lists items with definations pf corporate rules, constraints and guidelines. Architecture Principles can be categorized into Business, Data, Application or Technology principles. Rationale describe the business benefit with relationships to other principles and implications describe the business impact, requirements like resources or costs, implementation actions or consequences of adapting the principle.

Examples of Architecture Principles are listed in the table below.

SAP Intelligent Enterprise Architecture Solution Context
Enterprise Architecture Solution Context diagrams show relationships between business capabilities of desired solutions, organization with involved business units, users or roles and existing solutions.
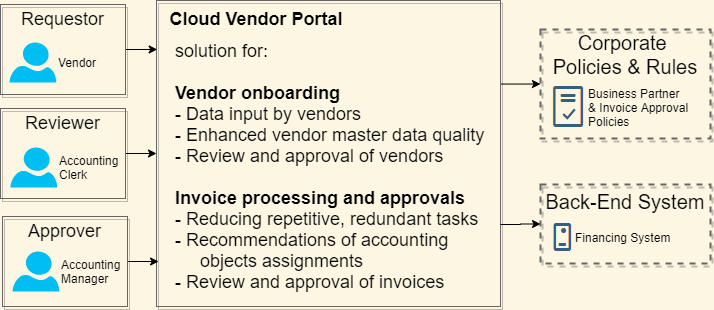
SAP Enterprise Architecture Solution Concept
The SAP Enterprise Architecture Solution Concept describes what we want to do to implement the SAP Intelligent Enterprise Architecture solution. Functional ABBs are high level, non-technical representations of needed business capabilities of the solution context with regard to Architecture Principles and systems described of the Baseline Solution Architecture.
SAP Enterprise Architecture - Risk Analysis
Risk Analysis is an ongoing task which starts with classifying identified risks with initial levels of impact like High, Medium or Low. After planning mitigation actions, risks can be classified with residual levels.

Additional risks might be identified in later ADM phases like for specific solution components.
Work products of the SAP Enterprise Business Architecture phase describe how the enterprise needs to operate to achieve the business goals with alignment of business and IT. The target business architecture represents the desired business capabilities in the context of the project.
SAP Enterprise Architecture - Business Capability Map
SAP Enterprise Architecture Business Capabilities Maps structure business architectures into Business Domains, Business Areas and Business Capabilities like the example diagram below with capabilities required for a digital supply chain multi-cloud portal solution.

The SAP Enterprise Information System Architecture describes IT Systems with combined aspects of application and data domains based on the Statement of Architectural work and Solution Concept. Work products of this phase deliver the target application and data architecture with diagrams which map Architectural to Solution Building Blocks. The SAP Enterprise Target Technical Architecture acts as input for the gap analysis which reflects differences between base and target architectures.

Applications represent logical groups of capabilities which manage data objects of data architectures to support business functions of the Business architecture.
SAP Enterprise Architecture - Solution Capability Map
Solution Capability Maps are realizations for Business Capability Maps. The example map below demonstrates a multi-cloud portal solution on SAP BTP and Microsoft Azure with S/4HANA Cloud RSA content for some solution capabilities of the inventory and transportation management business areas.

SAP Enterprise Architecture - Conceptional Data Diagram
Complements information flow defined in SAP Enterprise Architecture Data Flow Diagram of the SAP Intelligent Enterprise Architecture. The diagram outlines the relationship between data and business objects. Entities, attributes and their relationships with cardinality describe how information has to be processed.
Describes abstract data entities (with information objects as concrete representation) stored with different, also external, SBB. Conceptional Data Diagrams can be modelled with Entity Relationship or UML diagrams.
SAP Intelligent Enterprise Architecture Software Distribution Diagram
SAP Enterprise Architecture Software Distribution Diagrams visualize the distribution of SBB and identifies their deployment environments (on-premise / cloud) within the SAP Intelligent Enterprise Architecture.
Software Distribution Diagrams use information from baseline solution architecture for existing building blocks and vendor-specific information of solution realization diagram. The visualization of data flows can help to understand latency or network requirements.
SAP Enterprise Architecture Technology Architectures describe target architectures from deployment perspective, considering technology components (hardware and software) and their relationships. Technology architecture gaps have to be analysed to identify missing or inadequate hardware, software or infrastructure components between base and target technology architecture.

SAP Intelligent Enterprise Environments & Location Diagram
SAP Enterprise Architecture Environment and Location diagrams group technology components, including operating systems and network components into deployment environments. They visualize deployment locations with geographical information and interactions of SAP Intelligent Enterprise Architecture building blocks together with relevant runtime environments of SBB and network details.
SAP Enterprise Architecture Environment and Location diagrams identify locations of users, existing building blocks and deployment environments of target building blocks. Building blocks get grouped based on data center locations. The visualization of data flows can help to understand network requirements.
Key artifacts for the Opportunities & Solutions phase E are Architecture Roadmaps which describe how to fill the gaps between base and target solution with intermediate Transition Architecture steps for incremental implementations and fitting solution building blocks.
Fit-Gap analysis based on the baseline solution architecture helps to identify needed changes to introduce new SBBs or replace existing functional components. Functional dependencies of SBB get identified as well as user / role relationships, derived from the solution context.
Business Architecture Roadmaps visualize business outcomes and Application Architecture Roadmaps the solution implementation required to realize the business functionalities.
SAP Intelligent Enterprise Architecture Roadmap
The roadmap shows a project planning overview of action items with a timeline when to realize the SAP Intelligent Enterprise Architecture solution. Sequences outline the progress from baseline to target architecture with milestones associated to business value.
Work packages are identified together with their business value and prerequisites. Furthermore they get categorized according to their capabilities, described in the Solution Context and the scope of the statement of architectural work.
Template: diagram shows business values delivered within timeline on x-axis and capabilities on y-axis, with a sequence of work packages and their dependencies
Specific implementation aspects are covered in the remaining phases. The output of Phase F is a detailed implementation and migration plan. Implementation Governance monitors the implementation progress in Phase G and the Architecture Change Management process gets established in Phase H.
The Architecture Content Framework provides three categories of work products Deliverables, Artifacts and Building Blocks with guidelines and best practices on how to create these work products in the ADM phases. Work products describe the architecture of these phases in their context holistically, enable communication between business and IT, support decision taking and act as foundation for implementation and operation.
Deliverables are contractually specified, relevant and have to be signed of by stakeholders. Artifacts are work products such as lists (catalogs), matrices or diagrams. Sample artifacts are Solution Concept diagram, Architecture Principles catalog or Stakeholder Map matrix
Building blocks represent combinations of artifacts, typically hierarchically composed with different level of detail. They are categorized into Architectural Building Block (ABB) as functional components and Solution Building Blocks (SBB) which define product or vendor-aware implementation details to realize the target architectures of enterprises with best practices and a standardized architecture development process.
The Enterprise Continuum classifies work products managed as content within the Architecture Repository. This classification approach specifies architectures and solutions, from generic to specific with 4 states, to describe the evolution of building blocks. The Solution Continuum represents solution implementations on corresponding levels of the Architecture Continuum.
SAP Intelligent Enterprise Architecture is focused on the specific areas of the Architecture and Solutions Continuum with Enterprise Architecture and Solutions building blocks.
Agile Enterprise Architecture is an interative approach to operationalize innovation development with a combination of Design Thinking and Architectural Thinking. Use-case blueprint diagrams are key work products which support the transition from design to architectural thinking and vice versa. Agile innovation processes ensure viability to bring value with profitable and sustainable products, desirability to solve customer expectations and feasibility with operational capabilities.
Agile methods help to develop enterprise architectures to gain vision with temporary clarity and understanding in a VUCA world which is characterized with volatile, uncertain, complex and ambiguous antipodes. Agile Enterprise Architecture Management (EAM) reduces global coordination and control of leading SAP Architects. Agile EAM enables transformation with advised support and a more lightweight, less formalized, local and utility-centered approach.
The fundamental values of stability and sustainability remain valid, but they need to be adapted to the new requirements, such as short innovation cycles for technologies and business models.
Design Thinking is a creative approach which can add a user centric view to the Architectural Thinking method. The combination of user experience with enterprise architecture helps companies to transformat their business with innovations.
Establishing a broad architectural understanding to non-architects, enables different areas within the company, that are concerned with driving innovation, to make independent architectural decisions or evaluations for their SAP projects, but also stay compatible with the architectural framework with holistic and long-term considerations.
Agile SAP Enterprise innovation projects, which differentiate the business, require a rapid path to transform business ideas into values. In contrast to SAP projects, focused on operational excellence with focus on SAP core system maintenance, stability or efficiency. SAP Intelligent Enterprise Architecture development can handle different use cases with an IT of multiple speed layers.
Speed Layer 2 (Enterprise Mode) targets to improve operational excellence with proven business models, preserving stability and sustainability with compliance and standardization.
Speed Layer 1 (Pioneer Mode) performs sprints in agile SAP Intelligent Enterprise Architecture projects, exploring new business models with changing demands and new intelligent technologies. This layer enables exploration of innovate ideas with the concept of Minimum Viable Architecture, analogous to the concept of the Minimum Viable Product (MVP).
Based on the concept of the Last Responsible Moment (LRM), where reversible type 2 decisions are taken early to enable speed and non reversible type 1 decisions are taken as late as possible. Minimum viable architectures can ensure the compatibility to the operating, development and deployment environment, as preparation for operational excellence requirements like integration into existing SAP Enterprise architectures and security demands.
Creative thinking and architectural thinking are additional companion services for SAP Intelligent Enterprise Architectures, helping to operationalize innovation and to move the idea from speed layer one to speed layer two. Technical services are offered by the SAP Business Technology Platform to realize the architecture as result of the Creative Architectural Thinking process, to pull the idea from speed layer one to product market fit in speed layer two.
The Lean SAP Intelligent Enterprise Architecture approach is a tailored framework based on the TOGAF® standard without ADM phases and own diagram types such as Use Case Blueprint, Baseline Solution Architecture and Solution Realization.
The Value Discovery Cheat Sheet structures architectural work by identifying focus, value, approach and required technical capabilities.
Lean SAP Enterprise Framework Use-Case Blueprint
Based on the Scope of the Business Context, Use-Case Blueprints of the SAP Lean Enterprise Architecture Framework pivot from design thinking to architectural thinking. For each most valuable combination of user actions with key objective, scenes describe scenarios in storyboards from a user centric perspective and map user actions to target technical aspects with required data, involved applications and technical capabilities. Identified existing IT components and their relationship are input of SAP Enterprise Architecture Baseline Solution diagrams.
| Target Scenario | Actions | Required Data | Systems & Applications | Technical Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <user context> | <user action> | <data, attributes, type> | <list of systems and applications> | <highlight requirements> |
SAP Enterprise Architecture Baseline Solution
The SAP Enterprise Architecture Baseline Solution diagram describes existing building blocks, components and IT systems of the use-case blueprint diagram, their relevant dependencies to the target SAP Intelligent Enterprise Architecture, reuse options and integration requirements.
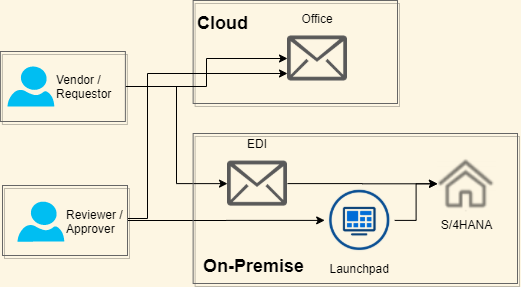
SAP Lean Enterprise Architecture Solution Realization
SAP Lean Enterprise Architecture Solution Realization diagrams add a more detailed level on technical requirements to deliver the solution and a vendor specific product mapping to the identified solution components. The target enterprise architecture defines the mapping of ABBs of the Solution Concept for applications and functional components to SBBs like SAP BTP, Azure or AWS cloud services.
The diagram considers inputs of the Statement of Architectural Work like defined cloud solution with preferred cloud providers of the Architecture Principles.
SAP Intelligent Enterprise Architectural Decisions
Documents discussion and outline decisions during the SAP Intelligent Enterprise Architecture project, with reasoning e.g. to track reasons of decisions against alternatives.
| Ref | Decision | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| <ID> | <short description> | <details about reason and possible considered alternatives> |
The SAP Business Technology Platform (SAP BTP) offers solution capabilities to implement Intelligent Enterprise Architectures as integrated end-to-end business processes or Data-to-Value scenarios. Database & Data Management, Analytics, Intelligent Technologies and Application Development & Integration services are part of SAP BTP Solution Concepts and provide solution capabilities to implement vendor agnostic ABB functionalities of Solution Contexts.
The SAP Business Technology Platform (SAP BTP) supports different kind of Intelligent Enterprise use-cases to optimize business in process & data, technology or innovation areas.
| ABB Functionality | BTP SBB Example |
|---|---|
| Data & Process Integration | SAP Cloud Plattform Integration Suite |
| Process Extension | SAP Cloud Platform Extension Suite |
| Process Management & Automation | Workflow Management |
| Business & Technical Services | Service Marketplace e.g. Service Ticket Intelligence |
| Digital Experience | e.g. Mobile, Portal services, Launchpad |
| Development Productivity | e.g. Business Application Studio, CAP, Transport Management |
| Data Layer e.g. cloud "Data Fabric" | corporate used components e.g. SAP Datasphere |