Well-architected Digital Supply Chains implement intelligent Design-to-Operate processes, with integrated hybrid multi-cloud SAP Manufacturing, Warehouse Management and Business Planning solutions:
The SAP S/4HANA Intelligent Enterprise is the central part of end-to-end Design-to-Operate processes based on the SAP Digital Supply Chain.
Design-to-Operate processes are composed of SAP Digital Supply Chain sub-processes from product design to asset operation:
Resilient SAP Digital Supply Chain architectures and implementations move intelligent Design-to-Operate processes from functional silos to agile, digital connected hybrid multi-cloud environments.
Digital supply chain environments make physical goods movements, assets or business documents visible as Digital Twins and enable collaboration of connected business partners within business networks.
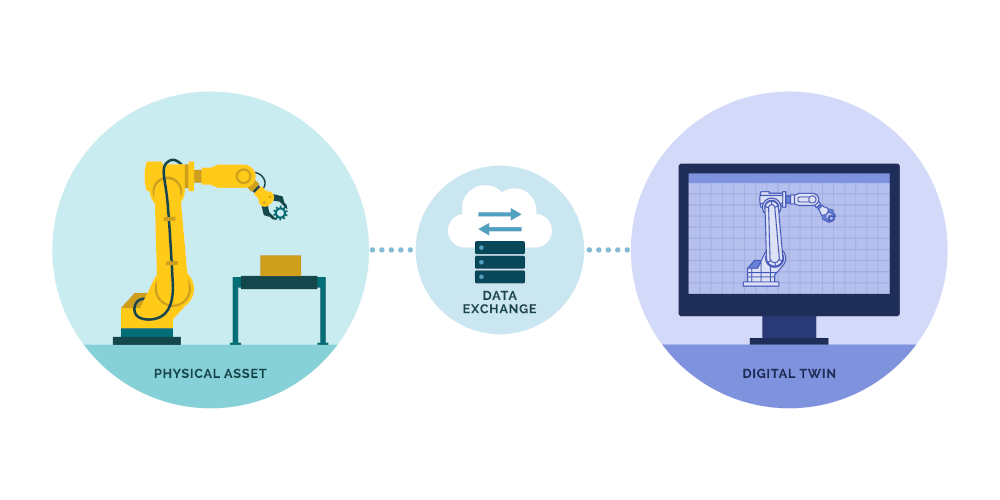
Integrated end-to-end business planning uses information provided by Digital Twins to support all product lifecycle phases with data-driven decisions.
Data-driven SAP S/4HANA digital supply chain processes implement innovations with emerging technologies like cloud services, IoT, AI Machine Learning (ML), RPA or real-time tracking to improve business decisions and automations. The information about business changes can be transferred, to all involved business partners within SAP Digital Supply Chain networks in real-time, with advanced communication patterns event-based, with notifications or handled by situations.
AI Machine Learning (ML) scenarios with predictions and automations enable intelligent SAP S/4HANA Design-to-Operate processes implements. SAP S/4HANA offers ready-to-use AI Machine Learning (ML) scenarios within the core system and custom AI/ML extensibility options on the Business Technology Platform (BTP).

Examples of SAP S/4HANA Digital Supply Chain AI machine learning (ML) scenarios are:
Predefined SAP S/4HANA Situation Handling templates for Manufacturing and Supply Chain use cases (with Fiori ID/ Scope Item):
Custom situations in digital supply chains can be implemented with the S/4HANA extended situation framework to react on e.g. modifications of asset or material master data.
BTP Intelligent Situation Automations can be implemented e.g. for Production Defects with business rules to inform production operators with mobile push notifications based on specific criteria or to perform analytics on defect handling.
SAP BTP Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a solution to automate repetitive tasks in supply chains with intelligent digital bots. Some Digital Supply Chain use-cases and predefined content of the RPA bot store are:
Hybrid multi-cloud architectures enable companies to build scalable and resilient digital supply chain management systems. Best practice architectures handle the increasing availability of information and turn data into value.
Multi-Cloud architectures integrate cloud services for e.g. data management, analytics, machine learning or process automations from multiple platforms like SAP BTP or Microsoft Azure. Hybrid multi-cloud architectures integrate supply chain processes vertically with cloud services and on-premise shop floor systems.
SAP Digital Supply Chain offers cloud solutions like S/4HANA Cloud, SAP Integrated Business Planning (IBP) and SAP Digital Manufacturing (SAP DM) with implementation best practices for integrated hybrid deployments.
Some examples of hybrid multi-cloud Digital Supply Chain with SAP solutions are:
Plan-to-Fulfill (P2F) is the Design-to-Operate sub-process which describes the journey of product-related information with three stages:
Integrated SAP Digital Supply Chain manufacturing systems offer real-time insights based on acquired data with visualized resource availability, analytics and reporting. These insights allow data-driven production scheduling to react fast on changing demands.
Production orders are digital business documents which contain all information to plan production processes. They have to be exchanged between integrated supply chain systems.
Releasing production order starts manufacturing processing and triggers the creation of related material, accounting and controlling documents to perform material movements with related financial operations. Production orders become cost objects for consumption (expenses) postings of actual material costs during the manufacturing process.
Three main steps in digital supply chain manufacturing execution are:
S/4HANA Digital Supply Chain, SAP Digital Manufacturing and Hyperscaler cloud services can be integrated hybrid multi-cloud architectures. These supply chain solutions solve individual manufacturing business requirements like 24/7 availability, support of large production facilities or scalability.
Supply chain cloud and on-premise environments offer complementary features. Cloud solutions are scalable to process changing data loads with high availability defined by SLAs. But cloud services can't guarantee 24/7 availability with consistent transfer rates and response times for critical manufacturing processes.
Digital Manufacturing edge deployments of mission critical components can increase the availability of manufacturing environments, with failover scenarios running production processes offline on-premise on the shop floor.
SAP Digital Supply Chain Warehause Management
SAP warehouse management systems control goods movements like staging to production, transfer of finished products or subassemblies.
Digitalization automates and accelerates warehouse processes with integrated systems or assets e.g. to automate bookings with IoT realtime tracking systems or work paperless with mobile apps.
SAP offers digital supply chain warehouse management solutions embedded in S/4HANA or as side-by-side installations. SAP Extended Warehouse Management (EWM) is the strategic warehouse management solution which offers integration options e.g. with other S/4HANA Digital Supply Chain modules (e.g. TM, QM) or cloud solutions like DMC.
SAP Digital Manufacturing (SAP DM) EWM Integration
Cross-order staging with the DMC Material Staging 2.0 app enables the advanced SAP Digital Manufacturing (SAP DM) EWM Integration scenario to supply components to production supply areas (PSA) to be used by any active production order.
Goods Receipt from production is another SAP Digital Supply Chain SAP DM EWM Integration example which starts with a packing unit as input of the Goods Receipt HU, followed by a inbound delivery created in EWM and finalized with the Goods Receipt for the production order in S/4HANA.
With MES-Driven Staging the process is planned with a staging request in Digital Manufacturing (SAP DM) mapped to the EWM warehouse request of internal stock transfer type. The staging progress with status of the EWM warehouse tasks is visible in SAP DM and EWM.
S/4HANA Transportation Management (TM)
S/4HANA introduced the transportation modules Basic Shipping (as successor of LE-TRA) and Advanced Shipping. Advanced Shipping offers optimizers like Vehicle Scheduling and Routing (VSR) to find the best way for a route with stops, Load Optimizer to arrange pallets or packaged based on master data settings.
Vehicle Scheduling (VSS) optimizes times considering available time windows, vehicle availability, operating times and scheduling directions. Embedded Scheduling is available for Basic Shipping with almost same functionality as VSS, but does not support customizing of scheduling constraints.
S/4HANA Transport Management implements the TM-EWM integration simplified with a single Freight Order object. Furthermore, Advanced Shipping & Receiving (ASR) outbound processing is improved by automatic consignment building and delivery split functionalities.
Unified package building (UPB) acts as generic layer for packaging specifications, packing instructions and package builder engines. UPB is used by TM, EWM (e.g. Synchronous GR PO) and Logistics General (LO) S/4HANA components.
Unified package building is integrated in EWM inbound delivery processes with apps (Create/Change Inbound Delivery) and RF transactions (Unloading, Receiving Handling Units) with packaging materials proposals.
SAP S/4HANA DSC integrates supply chain planning, manufacturing and logistics modules. SAP EWM, SAP S/4HANA ePP/DS, SAP S/4HANA PEO, Transportation Management (TM), Yard Logistics and eSPP can be deployed in-stack or as side-car with S/4HANA on-premise or PCE with same code line.

S/4HANA DSC offers synchronous and asynchronous options to integrate other digital supply chain solutions like IBP or SAP DM.
Some integration highlights are synchronous OData APIs for planning data, orders (planned, production, process), confirmations and PIR. Asynchronous integrations with SOAP messages (manufacturing orders) or business events (production or process orders, products, product allocations).
PEO comprises production engineering and production operations business areas.
Some PEO high level characteristics are:
Production engineering:
Production Operations:
SAP Digital Supply Chain Asset Management solutions improve asset performance and maintenance. The visibility of digital real-time insights enables supply chain process automation.
Some automation examples are:
SAP Intelligent Asset Management (IAM) offers cloud-based solutions to manage asset supply chain lifecycles digitally.
Asset Intelligence Network (AIN) offers shared data within asset networks to enable collaboration and data-driven decisions of business partners based on the Asset Central Foundation data layer.
SAP Asset Performance Management (APM) is a SaaS BTP solution with Asset Strategy and Asset Health capabilities. APM is seamlessly integrated with SAP EAM with synchronized master and transactional data. Furthermore, SAP GUI transactions offer an Asset Central tab on equipment, functional location and notification level.
AI-based Predictive Maintenance is the part of Asset Performance Management which predicts maintenance and service needs to reduce downtimes by applying advanced analytics and machine learning on IoT data.
Failure modes describe how pieces of equipments can fail with type (e.g function not obtained - lost - out of limit or non-critical failure), subclass (e.g. Power Transformer inherits from Transformer class) and one or more categories (e.g. breakdown, vibration, start failed).
Equipment Health Indicators represented by a health curve with health conditions of equipment over time vizualize decreasing health for downtime planning.
The Machine Learning Engine provides Model Management for Health Indicator Data Sets, Failure Mode Analytics and Leading Indicators together with some configuration and validation capabilities.
SAP S/4HANA Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) offers demand processing, maintenance planning and execution capabilities. These capabilities enable maintenance end-to-end processes structured into 9 phases which simplifies the status management and progress tracking. Each of these phases is assigned to one individual role.
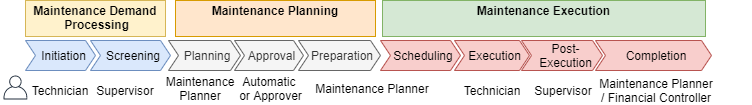
Scope items for Reactive (4HH), Proactive (4HI), Improvement (4VT), Operational and Overhead (4WM) provide best practices to guide users along the process.