The Lead-to-Cash process described on this page is part of the SAP S/4HANA system and integrates with other processes:
Lead-to-Cash (L2C) extends Order-to-Cash (O2C) processing with marketing and pre-sales steps, from customer's interest to buy to company's realization of revenue.
Best Practices for the SAP Intelligent Suite implement SAP S/4HANA ERP as digital core integrated with Sales and Customer Experience cloud solutions:
Lead-to-Cash process flow:

Sub-processes of the Lead-to-Cash are:
This sections provides an overview of innovation examples with different intelligent technologies. Introduced by Lead-to-Cash and Sales Monitoring and Analytics Roadmaps, with selected Best Practice scope items and Fiori apps.
Embedded SAP Analytics Cloud
The new simplified SD Status Data Model has moved status information from separated status tables to transactional document tables vbak, vbap, likp, lips.
SD Pricing has introduced:
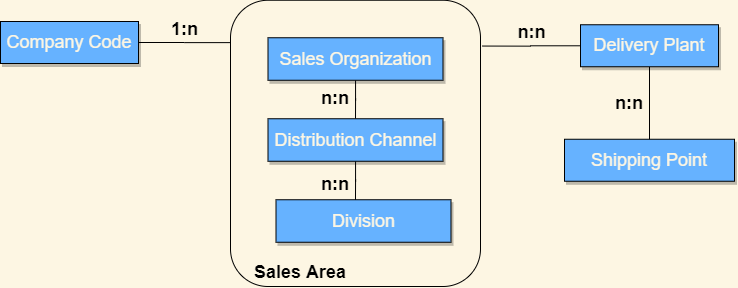
Three Business Partner Roles are assigned to customers:
Material Master Sales views are maintained with sales organization and distribution channel information.
Sales order processing can be started with pre-sales activities like customer sales inquiries (RFI) or quotations. These documents offer customers information about products, availability and prices, determined based on conditions. Multiple pre-sales documents can be combined into one sales order.
Sales Order Document
Master data includes
Item Schedule Lines correspond to deliveries containing quantities and dates
considered as customer independent requirements in MRP
Mandatory partner functions can be copied as default from the the customer master sales data
Financial Supply Chain Management (FSCM) ensure customers do not exceed their credit limit
Material availability is checked on plant level
Delivery Processing
Outbound deliveries are reference documents for sales orders. They initiate shipping processes with shipping points as responsible organizational units assigned to sales order items. Each sales schedule line becomes one item of a delivery document.
The relationship between sales orders and delivery documents depends on the concrete use case:
Transfer requirements are created for deliveries, when a warehouse number is assigned to the plant / storage location combination.
S/4HANA Backorder Processing (BOP)
Not covered demand of sales orders, with incomplete confirmed items or delivery dates which can't be kept, are called backorders. With backorder processing you can increase or decrease existing material confirmation for customers to solve availability problems.
The advanced Available-to-Promise Processing (aATP) functionality of S/4HANA offers BOP apps to check availability and confirmations, after changes of demand or supply in the order fulfillment process. BOP segments and variants define priorizations, sorting and settings for requirements for BOP runs.
Enhanced Warehouse Management (EWM)
Sales outbound deliveries trigger EWM warehouse requests of type outbound delivery order. Warehouse tasks are used to execute the physical goods movement.
Picking can be performed with collective processing of one worklist for different outbound deliveries.
After picking the goods EWM posts a goods issue to update:
Billing Document
The output of the internal billing document is the customer invoice as external document.
Posting of billing document creates:
The process starts typically with an order or delivery based transportation requirement. Transportation planning helps to optimize freight units, usage of resource, routes and costs.